Dermis – The human skin is a remarkable organ that acts as a protective barrier between the body and the exterior environment. Comprising three primary layers, namely the epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous tissue, the dermis plays a critical role in supporting and nourishing the skin. In this article, we will explore the dermis’s definition, structure, and functions.
Definition of Dermis
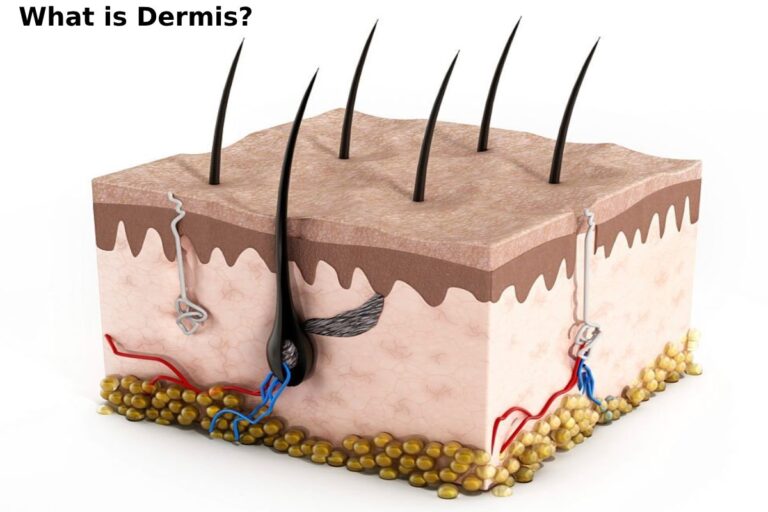
The dermis, also known as the corium, is the thickest layer of skin between the epidermis (the outermost layer) and the subcutaneous tissue (the deepest layer). It comprises connective tissue, blood vessels, nerve endings, hair sacs, sebaceous glands, and sweat glands. The dermis plays a crucial role in maintaining the skin’s integrity and elasticity, safeguarding it against mechanical stress, and providing essential nutrients and oxygen.
Also Read: Ketogenic Diet
Structure of the Dermis
The [dermis] is a complex and dynamic layer characterized by its dense collagen and elastic fibers network. It can be divided into two sub-layers: the papillary and reticular dermis.
- Papillary Dermis: Positioned as the uppermost layer of the dermis, the papillary dermis comprises loose connective tissue. It forms finger-like projections known as papillae that extend into the epidermis. The interaction between the papillary dermis and the epidermis creates the epidermal-dermal junction, contributing to the skin’s structural integrity. Additionally, the papillary dermis contains specialized cells called fibroblasts, which are responsible for synthesizing collagen and other extracellular matrix components.
- Reticular Dermis: Situated beneath the papillary [dermis], the reticular dermis constitutes most of the dermal layer. It is composed of dense irregular connective tissue, which contains a higher concentration of collagen fibers than the papillary [dermis]. These collagen fibers give the skin strength, elasticity, and structural support. The reticular [dermis] also houses blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, nerve endings, sweat glands, and sebaceous glands.
Functions
The [dermis] performs several crucial functions that are indispensable for maintaining healthy skin and overall body well-being:
- Support and Elasticity: The dense network of collagen and elastic fibers within the [dermis] offers structural support and elasticity to the skin. This property allows the skin to stretch and bounce back to its unique shape after being stretched, ensuring its resilience and flexibility.
- Nourishment: Blood vessels within deliver oxygen and nutrients to the skin cells, promoting cellular metabolism and growth. This ensures that the epidermis, the outermost layer, receives the necessary nourishment for constant renewal.
- Thermoregulation: The [dermis] contains blood vessels that are crucial in regulating body temperature. When the body is overheated, these blood vessels dilate, allowing heat to escape through the skin’s surface. Conversely, the blood vessels constrict in cold conditions, reducing heat loss and conserving body warmth.
- Sensory Perception: Numerous nerve endings in the [dermis] are responsible for sensing touch, pressure, pain, and temperature. These sensory receptors enable the perception of external stimuli and warn against potential harm.
Conclusion: The [dermis] is a fundamental component of the skin, responsible for its strength, flexibility, and overall health. Moreover, understanding the dermal layer’s structure and functions is essential for comprehending the complexity and resilience of this vital organ. Proper care and attention to the [dermis] can lead to healthy, radiant skin and a better understanding of how our body works to protect itself from external threats.